Los Angeles/DNA - The expansion of the BRICS group of nations into what has informally been named BRICS+ could highlight a geopolitical shift, with the new grouping positioning itself as a counterpoint to the Western-led geopolitical order, a report published by the Luskin School of Public Affairs at the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) argues.
The , titled "Towards A New Global Contestation? Comparing the Governance Performance of G7 and BRICS+ Nations" examines how the ten BRICS+ countries compare to the G7 nations on factors such as provision of public goods, quality of democracy and quality of governance. It uses the (BGI) to measure the governance performance of countries in these three dimensions.
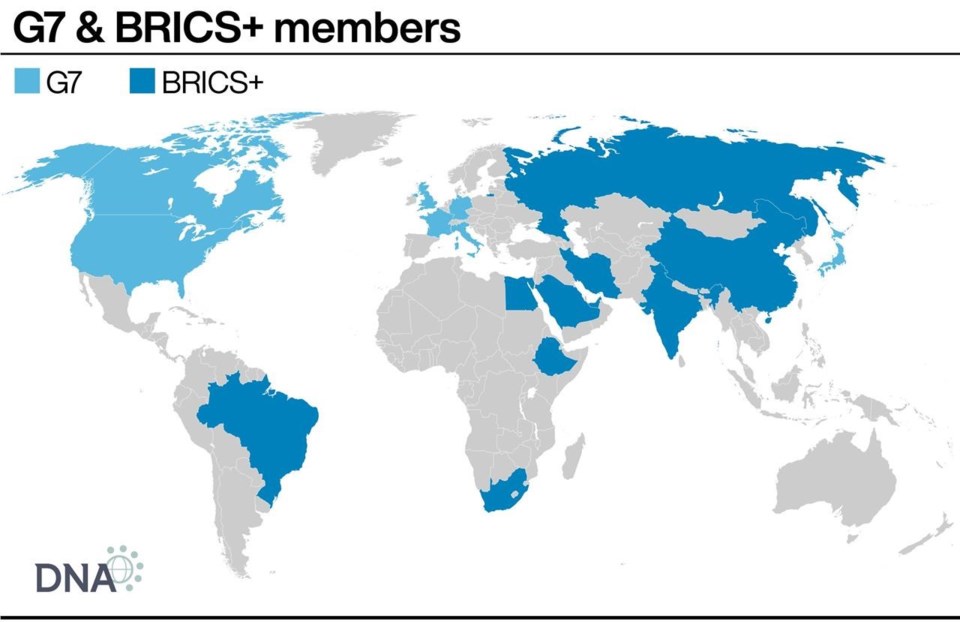
In January 2024, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Ethiopia, Egypt and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) joined the BRICS group.
The term BRICS was originally coined by an economist in the 2000s to refer to a group of emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and later, South Africa. Argentina's new president, Javier Milei, pulled the plug on his country joining BRICS+ in late December 2023. He said the decision to join had been taken by the previous government and had to be reviewed.
The BRICS+ have much larger combined population, which, at a rate of 7.8 per cent by 2025, is expected to grow twice as much as in the G7 countries (United States, Germany, France, Japan, Canada, Italy and the United Kingdom). At the same time, economic output and per capita GDP are lower than in the G7. The latter organisation also boasts greater soft power, a term used to describe the exertion of influence over other nations through attraction and persuasion, not coercion or force.
Over the coming years, the projected growth rates of the BRICS+ members are expected to enhance the group's economic clout. For example, Egypt's GDP is projected to increase by 635 per cent by 2050, the report says, quoting investment firm Goldman Sachs.
At the same time, the quality of democracy according to the BGI index has declined in India, Brazil (during the rule of President Jair Bolsonaro) and China, with authoritarian trends persisting particularly in China, Russia and Saudi Arabia.
According to the report, improvements in the provision of public goods have also been significant in some BRICS+ countries, even as state capacity and democratic accountability have declined. Overall, the authors conclude, the BRICS+ countries appear increasingly susceptible to authoritarian rule. "The G7's consistently high Democratic Accountability scores contrast sharply with the BRICS+ countries, where a noticeable trend towards centralized authority prevails", the report states.
New members have notably dragged down the average BRICS+ democracy accountability score, the report says, pointing to a "longstanding lack of meaningful checks on executive power". It cites Saudi Arabia as an example, arguing that its "absolute monarchy has consistently restricted all but the most basic political and civil rights of its citizens".
With an eye on the trends towards authoritarianism it identifies in most BRICS+ members, the report outlines two possible future scenarios.
In the first scenario, the government of a given country cannot sustain improvements in delivering public goods, possibly due to declining resources, high debts or other economic factors. As a result, most of the population grows dissatisfied with the quality of life. "However, authoritarian countries can remain in an uneasy suboptimal equilibrium for decades, as the history of the Soviet Union and Iran, among others, have shown", the report cautions.
The second scenario would see some or most of the BRICS+ members reach a quality of life comparable to that of liberal democracies. According to the authors, this would challenge the so-called "autocratic fallacy". According to this theory, authoritarian governance cannot effectively scale public goods, and broad-based prosperity is correlated with adherence to democratic principles.
The outcome of the second scenario would call into question the longstanding assumption, the report says, that democracy and the well-being of the population are the common aims of how countries develop. "It would shatter the belief in a growing global comity of wealthy and democratic countries", the report warns.
The report's findings also indicate that most BRICS+ members do not seek increasing confrontation with their G7 counterparts, and that they engage instead in a strategy that mixes cooperation and contestation. It is a way for them, the authors conclude, to take advantage of opportunities that may open up during the current uncertain geopolitical conditions, while at the same time mitigating risks: "Together with Brazil, India and South Africa, more of the new BRICS+ members may engage in fence-sitting and hedging behaviour rather than take clear and active sides in some fuller scale contestation or conflict."
The report already identifies some evidence of this trend: "Even China - which is seen in increasingly confrontational terms in the West - retains enormous economic links with its geopolitical adversaries at the same time as it deepens its alliance with Russia", it states. "Variations on this theme - such as the countries who rely on the US for external security and China for internal security - will likely only become more common in the rest of the 2020s."
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is not intended for publication, but contains notes for the recipients:
This text and the accompanying material (photos and graphics) is an offer from the Democracy News Alliance, a close co-operation between Agence France-Presse (AFP, France), Agenzia Nazionale Stampa Associata (ANSA, Italy), The 91原创 Press (CP, Canada), Deutsche Presse-Agentur (dpa, Germany) and PA Media (PA, UK). All recipients can use this material without the need for a separate subscription agreement with one or more of the participating agencies. This includes the recipient's right to publish the material in own products.
The DNA content is an independent journalistic service that operates separately from the other services of the participating agencies. It is produced by editorial units that are not involved in the production of the agencies' main news services. Nevertheless, the editorial standards of the agencies and their assurance of completely independent, impartial and unbiased reporting also apply here.
The 91原创 Press